The Role of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) in Shaping the Future of MarTech
The Data Fragmentation Challenge
Marketing departments today manage an average of fifteen different technology tools. Each platform collects customer information independently. Email systems track open rates and clicks. Website analytics monitor browsing behavior. CRM software stores purchase history and contact details. Social media tools measure engagement and sentiment.
This scattered approach creates problems that extend far beyond simple inconvenience. Marketing teams waste hours switching between platforms to build a complete picture of customer behavior. Data inconsistencies emerge when systems use different identifiers for the same person. Opportunities slip away because no single platform has enough information to trigger the right action at the right moment.
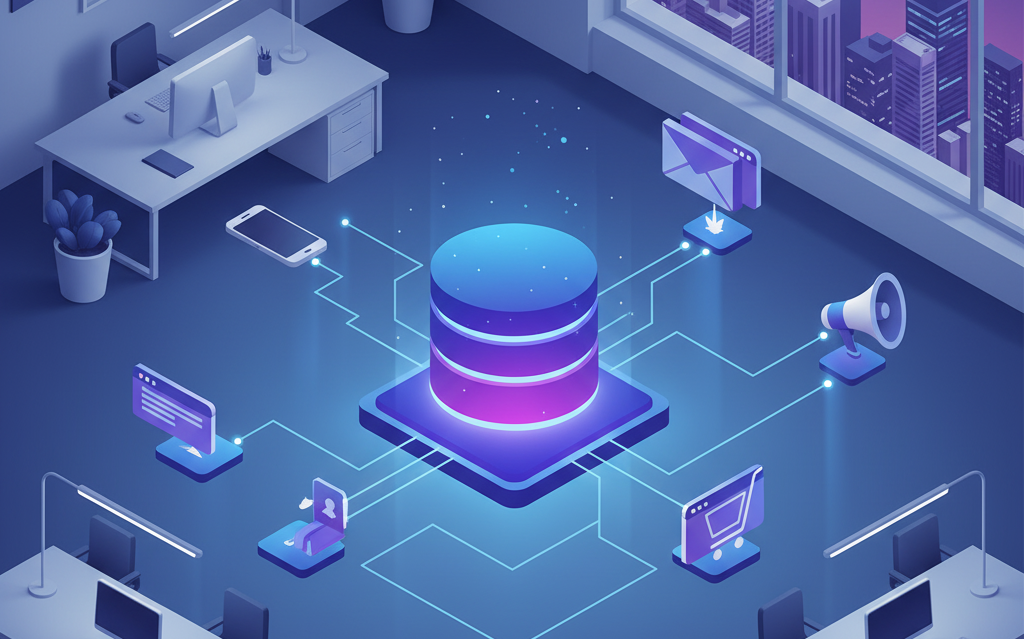
Customer Data Platforms address these fundamental challenges by serving as a central repository for all customer information. They connect disparate systems and create unified profiles that give marketing teams a comprehensive view of each customer’s journey.
Understanding CDP Architecture
A Customer Data Platform differs from other data management tools in several important ways. Unlike data warehouses designed for historical analysis, CDPs process information in real time. They capture customer actions as they happen and make that data immediately available to connected marketing tools.
CDPs also handle identity resolution automatically. When someone visits your website from a mobile device, opens an email on their laptop, and makes a purchase in your store, the platform recognizes these actions as coming from a single individual. It merges the data points into one coherent profile despite different devices, channels, and interaction types.
This unified view becomes the foundation for effective MarTech implementation. Every connected tool accesses the same accurate, up-to-date customer information. Marketing automation platforms, advertising systems, personalization engines, and analytics tools all work from a single source of truth.
Breaking Down Data Silos
Traditional marketing technology stacks operate in isolation. Your email platform knows what messages someone has received but cannot see their recent website behavior. Your advertising system targets users based on demographics but lacks insight into their purchase history. Your customer service team answers questions without knowing what marketing messages the caller recently received.
These silos prevent businesses from delivering consistent, relevant experiences across touchpoints. A customer might receive a promotional email for products they already purchased. Advertising continues after someone converts. Support agents repeat information already shared through other channels.
CDPs eliminate these disconnects by making customer data accessible across the entire marketing technology ecosystem. When implementing MarTech solutions, businesses that start with a strong CDP foundation avoid the integration problems that plague traditional approaches.
Product Siddha has worked with organizations that spent years accumulating marketing tools without a unifying data strategy. The process of connecting these systems through a CDP often reveals opportunities for optimization and consolidation that were previously invisible.
Real-Time Personalization Capabilities
Modern consumers expect businesses to recognize them regardless of how they interact with your brand. Someone browsing your website should see recommendations based on their email engagement history. A mobile app user deserves experiences informed by their in-store purchases. This level of coordination requires instant access to complete customer profiles.
CDPs enable this real-time personalization by continuously updating customer records as new information arrives. When someone abandons a shopping cart, the CDP immediately shares that signal with your email platform, advertising system, and website personalization engine. Each tool can respond appropriately based on the customer’s complete history and current context.
This capability transforms MarTech implementation from a collection of independent tools into a coordinated system that adapts to customer behavior moment by moment. The result is higher engagement rates, improved conversion rates, and stronger customer relationships.
Privacy and Compliance Management
Data privacy regulations have become increasingly strict across global markets. GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and similar laws in other jurisdictions impose serious obligations on businesses that collect and use customer information. Violations result in substantial fines and reputational damage.
Managing compliance across multiple marketing platforms presents significant challenges. Each system needs to respect customer consent preferences. Data retention policies must be enforced consistently. Customers who request data deletion require removal from every connected database.
Modern CDPs include privacy management features that simplify compliance. They maintain a central record of consent preferences and propagate those choices to all connected systems. When someone opts out of marketing communications or requests data deletion, the CDP ensures that preference applies across your entire technology stack.
This centralized approach to privacy management reduces legal risk while demonstrating respect for customer preferences. It also streamlines MarTech implementation by addressing compliance requirements at the platform level rather than configuring privacy controls separately for each tool.
Improving Marketing Attribution
Understanding which marketing activities drive results remains one of the most difficult challenges in the field. Customers interact with brands through multiple channels before making purchase decisions. They might see a social media ad, visit your website several times, read email newsletters, and talk to a sales representative before buying.
Traditional attribution models struggle to track these complex journeys accurately. They often credit the last touchpoint before conversion while ignoring the earlier interactions that built awareness and consideration. This incomplete picture leads to poor investment decisions as marketing teams allocate budget based on faulty data.
CDPs solve attribution problems by capturing every customer interaction across all channels and devices. They build complete timeline records that show exactly how marketing activities influence customer behavior over time. This comprehensive view supports sophisticated attribution models that recognize the contribution of each touchpoint throughout the customer journey.
Better attribution leads to smarter MarTech implementation decisions. Teams can identify which tools and channels generate the best returns and adjust their technology investments accordingly.
Predictive Analytics and Customer Insights
The volume of customer data collected by modern businesses exceeds human capacity to analyze manually. Valuable patterns hide within millions of interactions. Customer segments with similar behaviors and preferences remain unidentified. Opportunities to prevent churn or encourage upsells pass unnoticed.
Advanced CDPs incorporate analytics capabilities that uncover these hidden insights. They identify customer segments based on behavior patterns rather than simple demographic categories. They calculate churn risk scores that trigger retention campaigns before customers leave. They recommend products based on sophisticated algorithms that consider multiple factors beyond basic purchase history.
These predictive capabilities enhance the value of every connected marketing tool. Email platforms can target high-value segments identified by the CDP. Advertising systems can focus budget on customers most likely to convert. Customer service teams can prioritize outreach to accounts showing signs of dissatisfaction.
Product Siddha emphasizes that successful MarTech implementation requires more than just connecting tools. It demands a strategic approach to data that turns raw information into actionable intelligence.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Marketing teams spend considerable time on data management tasks that add little strategic value. Exporting lists from one system and importing them into another. Manually segmenting audiences based on criteria stored across multiple platforms. Reconciling conflicting information about the same customer. Troubleshooting integration failures between tools that should communicate automatically.
CDPs eliminate much of this busy work by handling data synchronization automatically. Marketing teams define rules for how information should flow between systems, and the platform executes those rules continuously without human intervention. Updates propagate instantly. Data stays consistent. Integration problems surface quickly with clear diagnostic information.
This operational efficiency allows marketing teams to focus on strategy and creativity rather than technical maintenance. They spend more time crafting compelling messages and designing effective campaigns, less time wrangling data between systems.
Building for Future Flexibility
Marketing technology evolves rapidly. New tools emerge that promise better performance or novel capabilities. Existing platforms release updates that change how they operate. Business requirements shift as companies enter new markets or launch new product lines.
Organizations that build their MarTech stack without a CDP foundation often find themselves locked into rigid configurations that resist change. Adding a new tool requires custom integration work. Switching platforms means rebuilding connections from scratch. Adapting to new business requirements involves significant technical effort.
CDPs provide flexibility by serving as a stable integration layer between your customer data and your marketing tools. Adding a new platform requires connecting it to the CDP rather than integrating it with every existing system. Replacing an underperforming tool involves redirecting data flows without rebuilding your entire stack.
This architectural approach reduces the long-term cost of MarTech implementation while increasing agility. Businesses can experiment with emerging technologies without fear of creating unmaintainable complexity.
Strategic Implementation Considerations
Deploying a Customer Data Platform requires careful planning. Organizations must define what data sources to connect, how to structure unified customer profiles, and which downstream systems to integrate. They need governance policies that specify who can access different types of customer information and for what purposes.
Starting with a focused scope often yields better results than attempting to connect everything at once. Identify the most critical data sources and the highest-value use cases. Build those connections thoroughly and ensure they deliver measurable business value. Expand the platform’s reach gradually as teams gain experience and confidence.
Product Siddha recommends that businesses evaluate their current marketing technology landscape before implementing a CDP. Understanding existing data flows, identifying redundant tools, and clarifying business objectives all contribute to a more successful deployment that delivers returns quickly while establishing a foundation for continued growth.